Product Overview
The NTC 10kΩ Thermistor is a highly sensitive temperature-sensing component that provides precise resistance variations in response to temperature changes. With a negative temperature coefficient (NTC), its resistance decreases as temperature increases, making it ideal for temperature measurement, compensation, and control applications. It is widely used in power supplies, battery management systems, home appliances, and industrial automation.
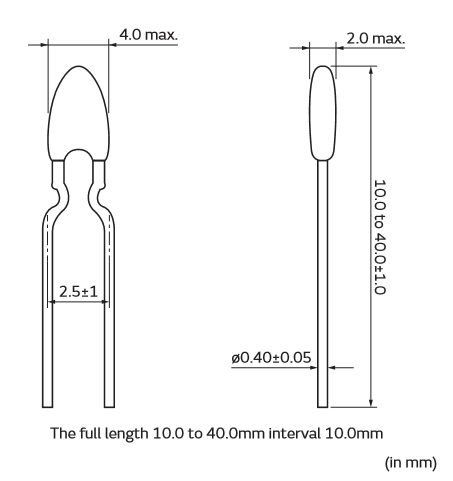
Key Features:
- Negative Temperature Coefficient (NTC) – Resistance decreases with increasing temperature.
- 10kΩ Resistance at 25°C – Standard for temperature-sensitive applications.
- High Sensitivity & Accuracy – Provides precise temperature readings.
- Fast Response Time – Quickly detects temperature changes.
- Wide Operating Range – Suitable for diverse environmental conditions.
- Compact & Durable Design – Ideal for embedded and industrial applications.
- Long-Term Stability – Ensures consistent performance over time.
Technical Specifications:
- Resistance at 25°C: 10kΩ
- Tolerance: ±1% to ±5% (varies by model)
- Beta Value (B25/50): 3950K (typical)
- Operating Temperature Range: -40°C to +125°C
- Thermistor Type: NTC (Negative Temperature Coefficient)
- Power Dissipation: 500mW (maximum)
- Response Time: Fast thermal response for accurate readings
- Mounting Type: Leaded or SMD versions available
Applications:
- Temperature Sensing & Measurement – Used in thermostats, temperature probes, and monitoring systems.
- Temperature Compensation – Adjusts circuit parameters based on thermal changes.
- Battery Management Systems (BMS) – Monitors battery temperature for safe operation.
- Home Appliances – Found in air conditioners, refrigerators, and water heaters.
- Power Supplies & Electronics – Provides thermal protection and feedback.
- Industrial Automation – Ensures proper functioning of machinery and control systems.
Why Choose the NTC 10kΩ Thermistor?
With high accuracy, fast response time, and reliability, the NTC 10kΩ Thermistor is an essential component for precise temperature sensing and control applications across various industries.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
EGP1.00
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
EGP0.25
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page
EGP0.25
This product has multiple variants. The options may be chosen on the product page









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.