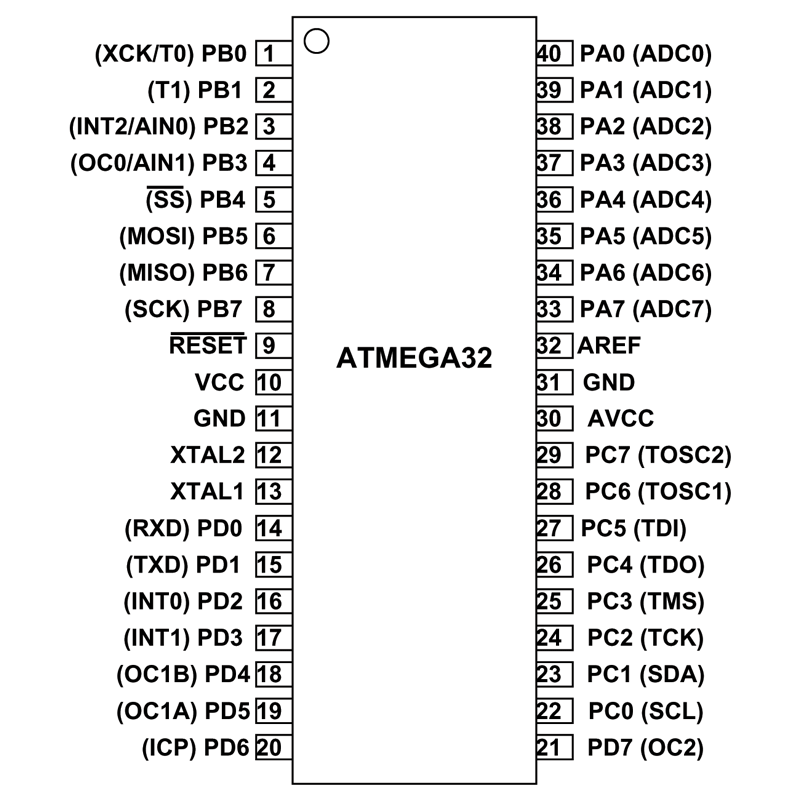
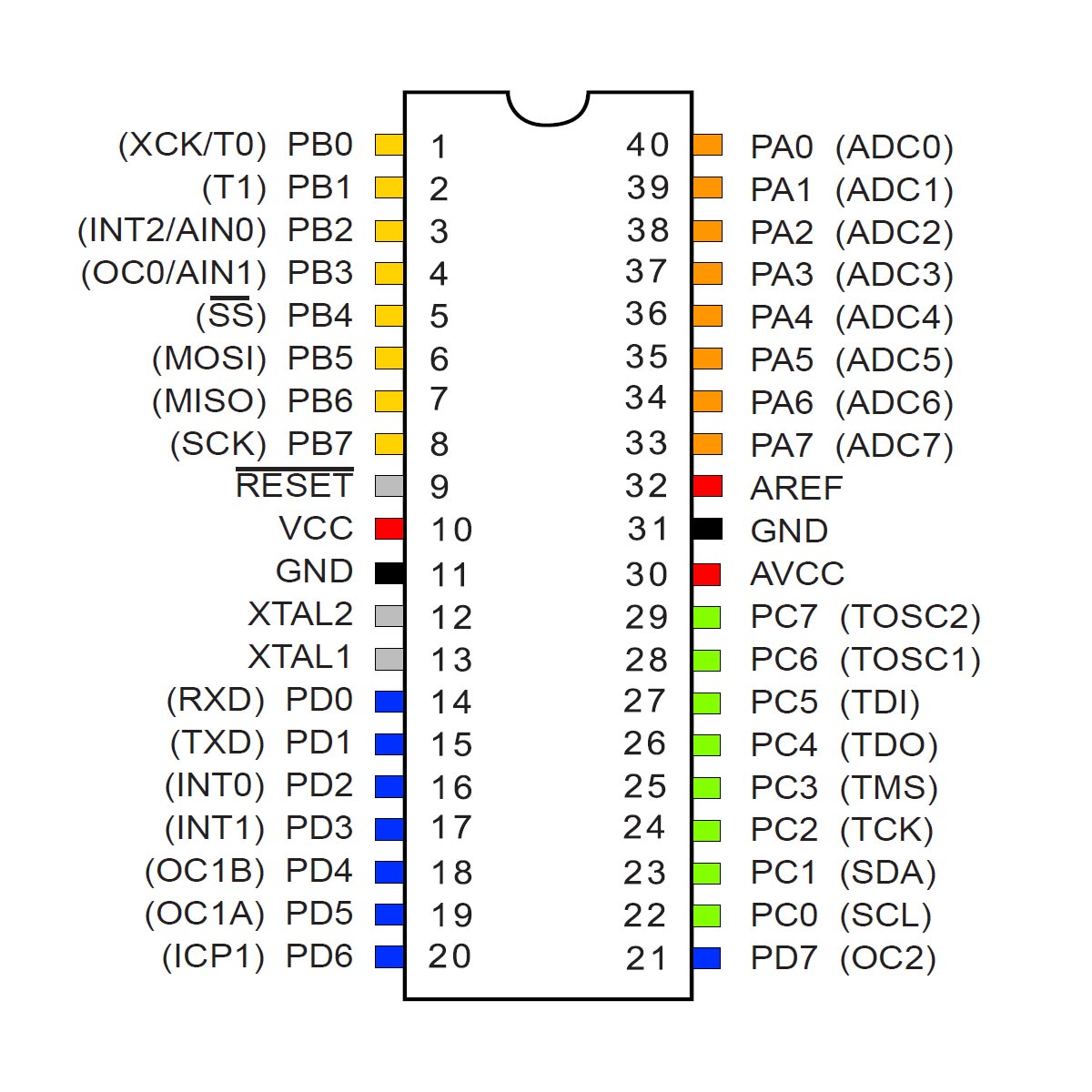
ATMEGA32 Pin Configuration
Pin No. Pin name Description Alternate Function
1 PB0(XCK/T0) Pin 0 of PORTB T0( Timer0 External Counter Input)
XCK ( USART External Clock I/O)
2 PB1(T1) Pin 1 of PORTB T1(Timer1 External Counter Input)
3 PB2(INT2/AIN0) Pin 2 of PORTB AIN0(Analog Comparator Positive I/P)
INT2( External Interrupt 2 Input)
4 PB3(OC0/AIN1) Pin 3 of PORTB AIN1(Analog Comparator Negative I/P)
OC0 (Timer0 Output Compare Match Output)
5 PB4(SS) Pin 4 of PORTB SS (SPI Slave Select Input). This pin is low when controller acts as slave.
[Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] 6 PB5(MOSI) Pin 5 of PORTB MOSI (Master Output Slave Input). When controller acts as slave, the data is received by this pin. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] 7 PB6(MISO) Pin 6 of PORTB MISO (Master Input Slave Output). When controller acts as slave, the data is sent to master by this controller through this pin. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] 8 PB7(SCK) Pin 7 of PORTB SCK (SPI Bus Serial Clock). This is the clock shared between this controller and other system for accurate data transfer. [Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) for programming] 9 RESET Reset Pin, Active Low Reset Pulled HIGH to RESET controller.10 Vcc Vcc = +5V
11 GND GROUND
12 XTAL2 Connected to Crystal Oscillator
13 XTAL1 Connected to Crystal Oscillator
14 PD0(RXD) Pin 0 of PORTD RXD (USART Input Pin)
USART Serial Communication Interface
[Can be used for programming] 15 PD1(TXD) Pin 1 of PORTD TXD (USART Output Pin)USART Serial Communication Interface
[Can be used for programming] 16 PD2(INT0) Pin 2 of PORTD External Interrupt INT017 PD3(INT1) Pin 3 of PORTD External Interrupt INT1
18 PD4(OC1B) Pin 4 of PORTD PWM Channel Outputs
19 PD5(OC1A) Pin 5 of PORTD
20 PD6(ICP) Pin 6 of PORTD Timer/Counter1 Input Capture Pin
21 PD7 (OC2) Pin 7 of PORTD Timer/Counter2 Output Compare Match Output
22 PC0 (SCL) Pin 0 of PORTC TWI Interface
23 PC1 (SDA) Pin 1 of PORTC
24 PC2 (TCK) Pin 2 of PORTC JTAG Interface
25 PC3 (TMS) Pin 3 of PORTC
26 PC4 (TDO) Pin 4 of PORTC
27 PC5 (TDI) Pin 5 of PORTC
28 PC6 (TOSC1) Pin 6 of PORTC Timer Oscillator Pin 1
29 PC7 (TOSC2) Pin 7 of PORTC Timer Oscillator Pin 2
30 AVcc Vcc for Internal ADC Converter
31 GND GROUND
32 AREF Analog Reference Pin for ADC
33 PA7 (ADC7) Pin 7 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 7
34 PA6 (ADC6) Pin 6 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 6
35 PA5 (ADC5) Pin 5 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 5
36 PA4 (ADC4) Pin 4 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 4
37 PA3 (ADC3) Pin 3 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 3
38 PA2 (ADC2) Pin 2 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 2
39 PA1 (ADC1) Pin 1 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 1
40 PA0 (ADC0) Pin 0 of PORTA ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) Channel 0
ATMega32 Pin Diagram
ATMEGA32 Features
ATMEGA32 – Simplified Features
CPU 8-bit AVR
Number of Pins 40
Operating Voltage (V) +4.5 to +5.5 V (+5.5V being absolute maximum)
Number of I/O pins 32
Communication Interface JTAG Interface(24,25,26,27 PINS)[Can be used for programming this controller]
Master/Slave SPI Serial Interface(5,6,7,8 PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller]
Programmable Serial USART(14,15 PINS) [Can be used for programming this controller]
Two-wire Serial Interface(22,23 PINS)[Can be used to connect peripheral devices like sensors and LCDs]
ADC Module 8 channels , 10-bit resolution ADC
Timer Module Two 8-bit counters, One 16-bit counter [Total three]
Analog Comparators 1
DAC Module Nil
PWM channels 4
External Oscillator 0-8MHz for ATMEGA32L
0-16MHz for ATMEGA32
Internal Oscillator 0-8MHz Calibrated Internal Oscillator
Program Memory Type Flash
Program Memory (KB) 32Kbytes[10000 write/erase cycles]
CPU Speed (MIPS) 16 MIPS
RAM Bytes 2KBytes
Data EEPROM 1024 Bytes
Watchdog Timer Programmable Watchdog Timer with Separate On-chip Oscillator
Power Save Modes Six Modes[Idle, ADC Noise Reduction, Power-save, Power-down, Standby and Extended Standby]
Operating Temperature -55°C to +125°C(+125 being absolute maximum, -55 being absolute minimum)
ATMEGA32 Replacements
ATMEGA16, ATMEGA8535
ATMEGA32 Alternatives
ATMEGA8, ATMEGA328p
Where to Use ATMEGA32
ATMEGA32 is easy to program AVR controller. With appreciable program memory it can satisfy most EMBEDDED SYSTEMS. With various sleep modes it can work on MOBILE EMBEDDED SYSTEMS. Along with 32 programmable Input/Output pins, it can interface many peripherals easily. With Watchdog timer to reset under error it can be used on systems with no human interference. With so many features with each appreciating other we can implement ATMEGA32 in many control systems.
How to Use ATMEGA32
Using ATMEGA32 is similar to any other microcontroller. Similar to them it is not Plug and Play digital ICs. For working of ATMEGA32, first we need to save the appropriate program file in the ATMEGA32 FLASH memory. After dumping this program code, the controller executes this code to create the response.
Entire process of using an ATMEGA32 goes like this:
List the functions to be executed by ATMEGA32
write the functions in IDE programs using relative language
(Usually Atmel Studio 6.2 for Windows7,
Atmel Studio 7 for Windows10 [ https://www.microchip.com/avr-support/atmel-studio-7 ])
(For these IDE the functions should be written in ‘C’ language)
After writing the desired program compile for error elimination using IDE.
Opt the IDE application to generate HEX file for the written program.
Choose the programming device (usually SPI programmer made for AVR controllers) which establishes communication between PC and ATMEGA32
Run the HEX file dumping software which is related to the chosen programming device.
Choose the appropriate program HEX file in the SPI or other programmer software.
Burn the HEX file of program in ATMEGA32 flash memory using this program.
Disconnect the programmer, connect the appropriate peripherals for the controller and power the sytem.
Applications
There are thousands of applications for ATMEGA32.
Temperature control systems
Analog signal measuring and manipulations.
Embedded systems like coffee machine, vending machine.
Motor control systems.
Digital signal processing.
Peripheral Interface system.
2D Model
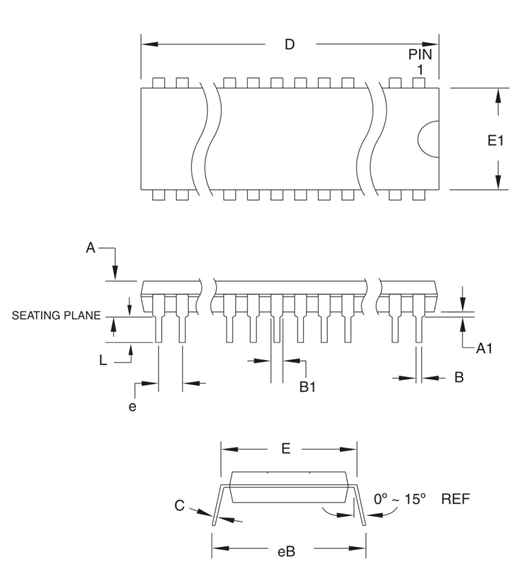 ,
, ,
, ,
,
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.








Reviews
There are no reviews yet.