Product Overview
The L295 Dual-Switch Mode Solenoid Driver IC is a high-efficiency dual-channel driver designed for controlling solenoids, relays, motors, and inductive loads. It features switch-mode operation, which significantly reduces power dissipation while ensuring high-performance control. With adjustable current regulation, thermal protection, and wide voltage operation, the L295 is ideal for industrial automation, automotive systems, and robotics applications.
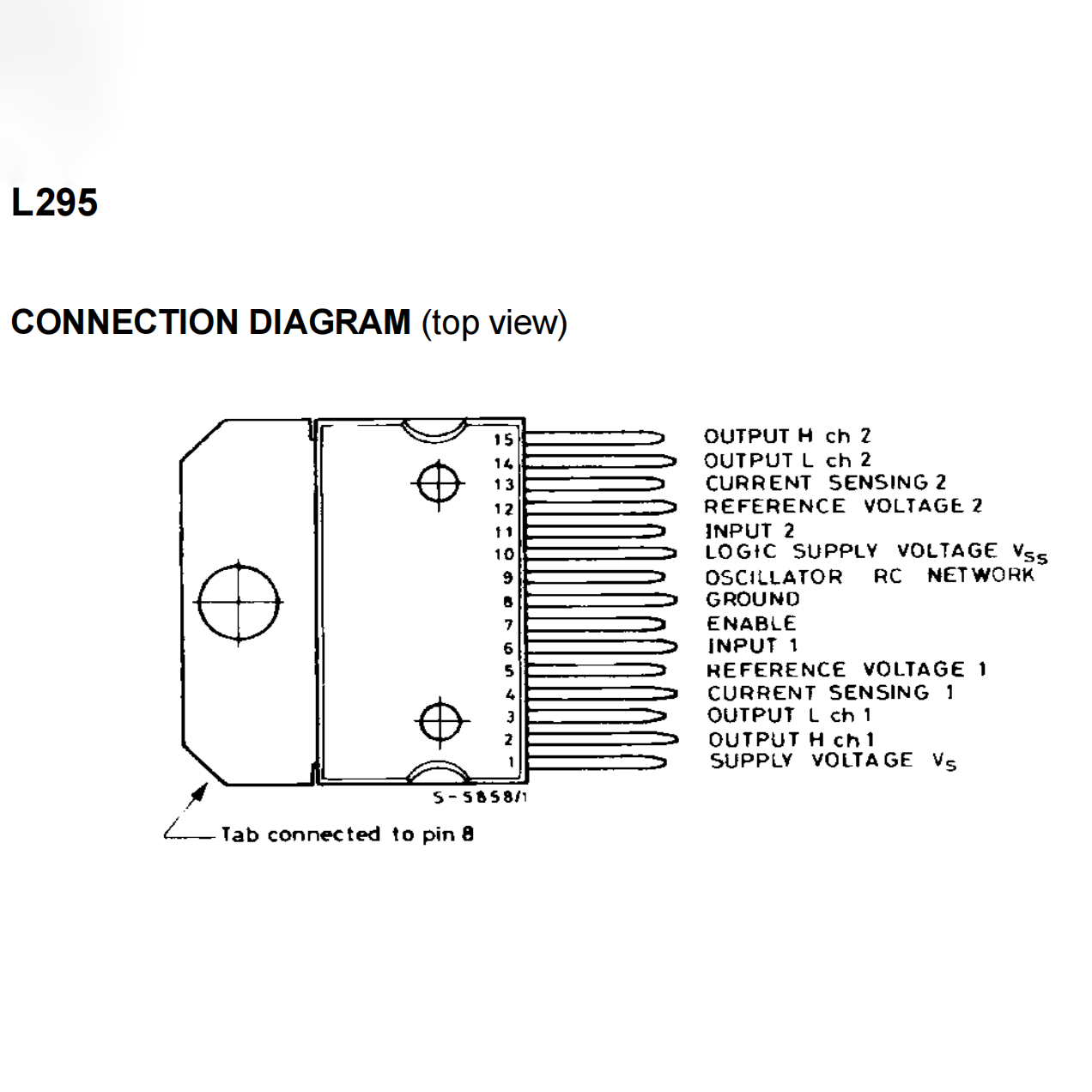
Key Features:
- Dual-Channel Driver – Controls two solenoids, relays, or motors independently.
- Switch-Mode Operation – Reduces power loss and improves efficiency.
- Adjustable Current Regulation – Enables precise control over the output current.
- Wide Operating Voltage Range – Supports 6V to 36V power supply.
- Overtemperature Protection – Prevents damage due to overheating.
- Overcurrent Limiting – Ensures safe operation with inductive loads.
- Compact Package – Available in a multi-pin PowerDIP package for easy integration.
Technical Specifications:
- Model: L295
- Number of Channels: 2
- Operating Voltage: 6V – 36V
- Maximum Output Current: 2A per channel
- Switching Frequency: Adjustable up to 20kHz
- Current Regulation: Adjustable via external resistors
- Protection Features: Thermal shutdown, overcurrent protection
- Power Dissipation: Reduced due to switch-mode operation
- Package Type: PowerDIP-15
Applications:
- Solenoid & Relay Control – Ideal for industrial automation and control systems.
- Automotive Systems – Used in fuel injectors, actuators, and other vehicle applications.
- Motor Drive Circuits – Provides efficient control for small DC motors.
- Robotics & Mechatronics – Ensures precise actuation of mechanical components.
- Industrial Equipment – Powers solenoids and electromagnetic devices with minimal heat dissipation.
Why Choose the L295?
With dual-channel control, efficient switch-mode operation, and built-in protection features, the L295 Solenoid Driver IC is an ideal choice for engineers looking for a versatile and power-efficient solution for controlling inductive loads.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.